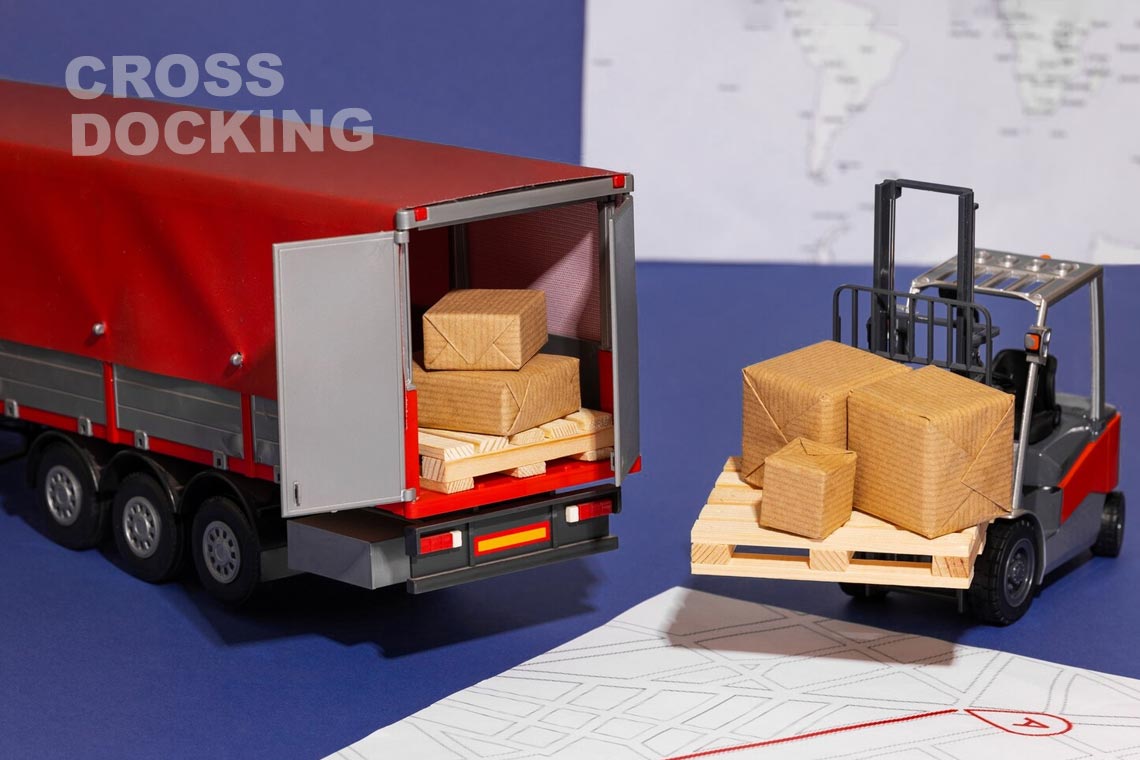
Logistics represents one of the most costly stages in business. The need to minimize the expenditure of time, resources, and personnel for delivery has led to the development of the concept of cross-docking. Let's consider the features, advantages, and variations of this technology in organizing logistics processes.
Cross-docking is a logistics model aimed at minimizing the time that goods spend in a warehouse. The main idea is for the warehouse terminal not to serve as long-term storage for goods, but rather for their prompt redistribution and optimization of freight flows. The term "cross-docking" accurately reflects the essence of this model, where goods intersect at the warehouse only for a moment before being sent further along the logistics chain.
This type of logistics performs a number of important tasks:
In logistics, there are two types of cross-docking depending on how shipments are assembled and what happens to the cargo in the warehouse:
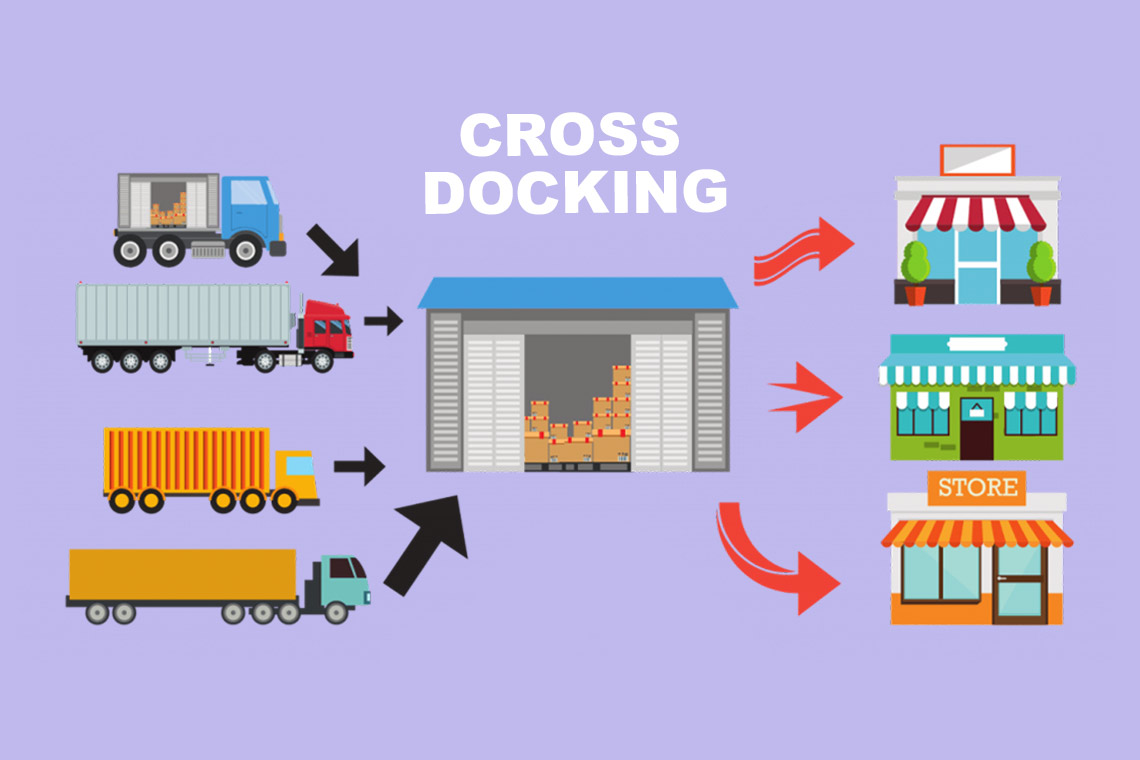
The distribution center in the USA is one of the key elements in the logistics chain, where goods undergo processing before being shipped to Amazon warehouses or other marketplaces. The choice of cross-docking method depends on the specifics of deliveries, cargo requirements, and customer requests. The cross-docking system for processing the flow of goods provides 2 schemes.
In this case, cross-docking is provided when there is only one recipient of the cargo. The packaging remains unchanged and is shipped in a single batch. When transferring part of the cargo between warehouses, each part must have a detailed list with information about the contents, recipient's address, and supplier.
This scheme involves processing incoming cargo, including consolidation and reconsolidation. For instance, part of the goods is sent from one city to another, with some of it possibly being packed differently and sent to another client. The cargo should be easily divisible into parts, each of which can be directed separately. Frequently, final orders are assembled with items already present in the warehouse and sent to the same client.
Undoubtedly, cross-docking has its advantages, and the main one is the reduction of delivery times. However, the system also has its drawbacks. Let's discuss this in more detail.
Main advantages:
But there are also disadvantages:
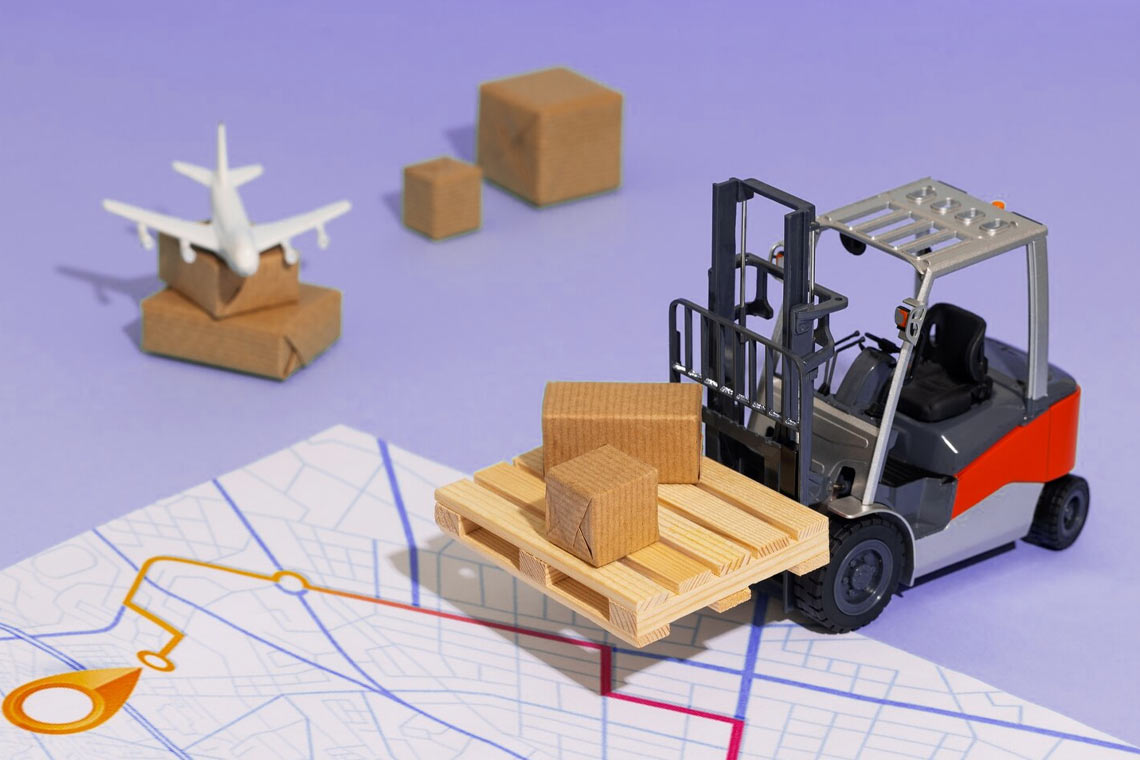

Cross-docking is a powerful tool for optimizing logistics processes and improving supply chain efficiency. To make the most of its potential, it is essential to carefully plan each stage of the process and choose a reliable partner. In addition to cross-docking, DiFFreight Company offers fulfillment, customs services, product inspection in China, warehouse services in Europe, and more. We provide a full range of services from a single logistics operator, which is very advantageous for your business.