
Article content:
The bill of lading is a crucial document in cargo transportation, commonly referred to as a bill of lading (B/L). Today, international logistics experts at DiFFreight will explain, in simple terms, how this document is prepared, why it is needed, and highlight its key challenges.
So, a bill of lading is a document that performs three functions:
Why Does This Document Exist? The logistics chain consists of multiple links. Before delving deeper, let’s clarify some terms:
The cargo owner is you. Since international transport ships carry thousands of cargo units, detailed accounting is essential to ensure the goods are delivered to the correct recipients.
Imagine you ordered a set of dishes from China to Ukraine, choosing maritime transport. Upon loading the ship, a bill of lading is issued to confirm receipt of the cargo, describe its type, status, and quantity. The document also states who will receive the cargo at the port of arrival.
Having explained what a bill of lading is and its functions, let’s explore its conditions. A B/L is a multi-page legal document describing:
The conditions of a bill of lading are standardized, complying with international regulations and protecting both the carrier and the shipper.
Example of a Bill of Lading
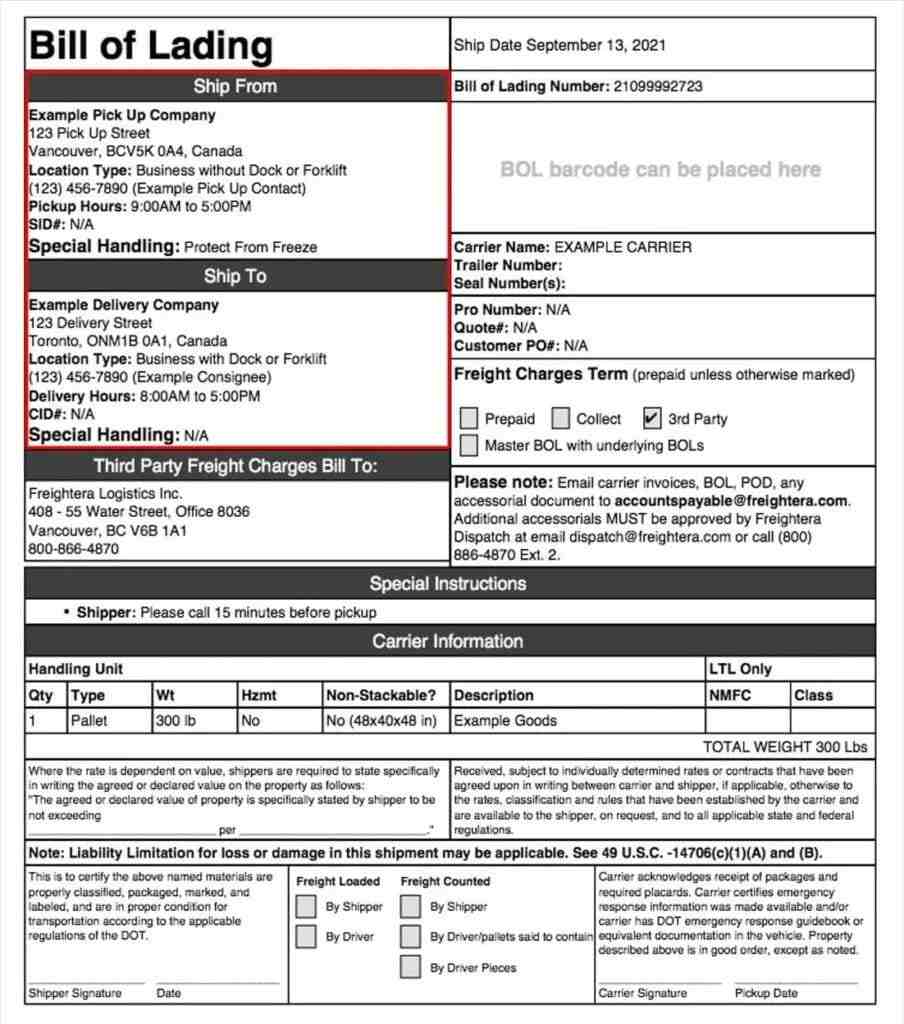
A bill of lading is the main document in sea transportation. Without it, disputes over cargo ownership and who is authorized to open the container would last indefinitely. The document serves as both a security instrument and a financial lever. A bill of lading prevents the cargo from being released at the port until the buyer has paid for it; banks require it as collateral when issuing loans, and lawyers use it as proof of the cargo’s condition at the time of loading.
The loss of a bill of lading is an administrative nightmare for everyone involved, leading to cargo blockage and substantial fines. Therefore, it is crucial to complete the document correctly to avoid ambiguities and unpleasant surprises during the logistics process.
Bills of lading are classified based on various criteria depending on their functions, features, and legal capabilities. While not all types will be covered here, we’ll highlight the most significant ones for transportation.
The first distinction concerns who issues the bill of lading:
The second aspect concerns the authenticity of the document:
Even notarized copies lack legal force. If multiple copies are needed, several originals are issued, marked as such. Typically, three identical originals are created—one for the sender (forwarder), one for the recipient, and one for the owner.
Given that cargo delivery from China to Ukraine often involves multimodal transport (using multiple modes of transportation), a multimodal (combined) B/L is prepared.
An electronic bill of lading (eB/L) is now available as a digital alternative to the paper document. It is stored and transmitted electronically through specialized platforms and systems. While this speeds up the exchange process, some companies still require physical originals.
Although the document's forms are standardized, they must be filled out correctly. It should include:
Creating this document requires knowledge of transportation laws, regulations, and technical procedures. It is advisable to use professional intermediaries or forwarders to avoid inaccuracies.
International logistics is expensive, and even minor errors can be costly:
For this reason, it is better to entrust preparation to professionals. DiFFreight offers customs brokerage services, including the preparation of essential documents.
Let’s set aside obvious cases of forged documents within a letter of credit or intentional fraud. Bills of lading are sometimes falsified to deceive carriers or recipients, but this does not happen when working with reliable parties. Below, we clarify certain types of documents that often cause confusion.
A negotiable bill of lading is commonly used in logistics, as it provides a more flexible method of transferring goods. It does not specify the consignee’s name.
With order or bearer types, the cargo is delivered to anyone with a corresponding bill of lading (electronic or paper) or the sender/consignee's authorization. In contrast, a non-negotiable B/L specifies a named consignee, prohibiting rights transfer to third parties.
This does not mean one type is inherently better. Each has its specific use case, and understanding this reflects the experience and professionalism of a logistics company.

If the goods are intact, a clean bill of lading is issued. A dirty B/L documents damage at the time of loading. If damages are discovered later and the B/L is clean, this creates confusion, especially regarding insurance. The nature of the damage and liability remains unclear.
Its scope extends beyond maritime transportation. For multimodal shipments, a combined marine B/L includes air or rail transport, though additional waybills are required for subsequent stages.
If you choose our company for sea freight, we will handle obtaining and processing all the necessary documents, including the bill of lading. Without it, sea delivery is simply impossible!
The process of obtaining it is multi-stage. In short, the original bills of lading are received against signature either at the office or at the port of departure in the local agency of the shipping line. Nowadays, electronic bills of lading are also used.
Entrust all cargo operations and document handling to DiFFreight — don’t dive into the intricacies of maritime logistics, wasting your time and resources.
The bill of lading is an important document in international trade. Proper preparation and understanding of its terms are key factors for safety and reliability in international shipping.
We invite you to a consultation with DiFFreight’s logistics professionals. Our brokers will prepare the bill of lading to minimize potential risks.
The bill of lading is an essential document in international trade. Proper preparation and understanding of its terms are crucial for safe and reliable international shipments.
We invite you to a consultation with DiFFreight’s logistics experts. Our brokers will prepare a bill of lading to minimize potential risks.